Difference between revisions of "Spring 2012:LFM Literature"
From Course Wiki
(Created page with "== Literature Search == Light field imaging allows for the capture of the light field of a sample in a single photograph.<ref>[http://graphics.stanford.edu/software/LFDisplay/lf...") |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | [[Category:Spring 2012]] | ||
| + | {{Template:Leanna20.345LFM}} | ||
| + | |||
== Literature Search == | == Literature Search == | ||
| Line 24: | Line 27: | ||
** With respect to this class, this is a novel project | ** With respect to this class, this is a novel project | ||
** Otherwise, this is not a new technology <ref name="Ref1996"/> but has been implemented into prototype microscopes in the past 7 years | ** Otherwise, this is not a new technology <ref name="Ref1996"/> but has been implemented into prototype microscopes in the past 7 years | ||
| + | |||
| + | == References == | ||
| + | <references/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{Template:20.345 bottom}} | ||
Latest revision as of 15:59, 17 May 2012
Literature Search
Light field imaging allows for the capture of the light field of a sample in a single photograph.[1] This has been recently commercialized in the Lytro Camera[2] which obtains a light field using a microlens and allows for processing of the image afterwards.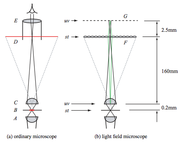
Light Field Microscope Diagram from the Stanford 2006 paper.[3]
They also documented their setup in more detail in a technical memo.[4]
Introduction to LFDisplay.[5]
Light field rendering.[6]
In 2009, the group published a better quality machine 4D Microscopy[7]
Objectives
I would be thrilled to work on this project for a number of reasons:
- It will force me to work on image processing, I am novice status :p
- It would be an awesome project
- It is feasible
- Only one additional physical component in a traditional bright field microscope
- Lots of code
- It is relevant
- This microscope can be used to compose a 3-dimensional image of the sample
- Taking 3-dimensional images quickly is a current point of interest in microscopy today
- It is novel
- With respect to this class, this is a novel project
- Otherwise, this is not a new technology [6] but has been implemented into prototype microscopes in the past 7 years
References
- ↑ A practical introduction to light field microscopy - Stanford 2010 (pdf)
- ↑ Light field camera
- ↑ Light field microscopy - Stanford 2006 (pdf)
- ↑ Optical recipes for light field microscopes - Stanford 2006 (pdf)
- ↑ LFDisplay: A real time system for light field microscopy
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Light field rendering - Stanford 1996
- ↑ Recording and controlling the 4D light field in a microscope - Stanford 2009 (pdf)