|
|
| Line 107: |
Line 107: |
| | |} | | |} |
| | | | |
| | + | ==Capture, save and examine images in Matlab== |
| | + | {|class="wikitable" |
| | + | |width="250"|[[Image: 140730_Matlab_01.png|frameless|250px]] |
| | + | |align="left"| |
| | + | * Log on to the computer and run <tt>imaqtool</tt> in Matlab. |
| | + | * Select the ''Manta GigE Mono 12" hardware in the left bar. |
| | + | * The ''Start Preview'' button will bring up a window of the live image from the CCD camera. |
| | + | * Move the lens and USAF 1951 target object to produce a focused image. |
| | + | * Measure the distance <math>S_o</math> from the target object to the lens and the distance <math>S_i</math> from the lens to the CCD active imaging plane. |
| | + | |- |
| | + | |width="250"|[[Image: 140730_Matlab_02.png|frameless|250px]] |
| | + | |align="left"| |
| | + | * Save images in Matlab: |
| | + | ** Make sure you limit to 1 the number of ''Frames Per Trigger'' in the ''General'' tab of the ''Acquisition Parameters''; |
| | + | ** Use the ''Start Acquisition'' and ''Export Data'' buttons; |
| | + | ** Navigate to the ''Student Data\ Fall 2014\'' directory accessible from the computer desktop to be able to access your data remotely, from your home computer for instance. |
| | + | |- |
| | + | |width="250"|[[Image: 140730_Matlab_03.png|frameless|250px]] |
| | + | |align="left" |
| | + | |- |
| | + | |width="250"|[[Image: 140730_Matlab_04.png|frameless|250px]] |
| | + | |align="left" |
| | + | |- |
| | + | |width="250"|[[Image: 140730_Matlab_05.png|frameless|250px]] |
| | + | |align="left" |
| | + | |} |
| | | | |
| | {{:Optical microscopy lab wiki pages}} | | {{:Optical microscopy lab wiki pages}} |
Revision as of 21:52, 30 July 2014
20.309: Biological Instrumentation and Measurement
Through this exercise, you will
- learn the basics of mounting, aligning and adjusting optical components;
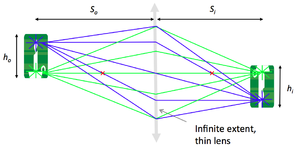
- verify the lens maker and the magnification formulae:
- $ {1 \over S_o} + {1 \over S_i} = {1 \over f} $
- $ M = {h_i \over h_o} = {S_i \over S_o} $
- become familiar with image acquisition and distance measurement using the Matlab software.
Build the optomechanical testing apparatus
To measure the relationship between $ S_o $ (the distance between the object and the lens), $ S_i $ (the distance between the lens and the image), $ h_o $ (the size of the object) and $ h_i $ (the size of the image), you'll need the following components:
- 1 x SPW602 spanner wrench
- 1 x SPW801 adjustable spanner wrench
- 1 x 3/16 balldriver for 1/4-20 cap screws
- 1 x 0.050" hex balldriver for 4-40 set screws
- 2 x RLA1800 dovetail optical rails
- 4 x RC1 rail carriers
- 8 x 1/4-20 x 5/16" cap screws
- 4 x PH2-ST post holders
- 4 x TR2 optical posts
- 4 x 8-32 set screws
- 1 x red LED
- 1 x LCP01 cage plate
- 2 x SM2RR retaining rings
- 1 x LCP02 cage plate adapter
- 1 x plano-convex f = 25 mm lens
- 4 x ER1 cage assembly rod
- 8 x 4-40 set screws
- 6 x SM1RR retaining rings
- 1 x R1DS1N 1951 USAF test target
- 1 x SM1L10 lens tube
- 1 x SM1RC lens tube slip ring
- 1 x LB1811 biconvex f = 35 mm lens
- 1 x CP02 cage plate
- 1 x Manta CCD camera
- 1 x 1/4-20 set screw
- 1 x Calrad 45-601 power adapter for CCD
- 1 x ethernet cable for CCD
|

|
|

|
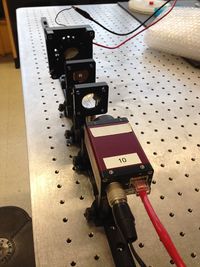
* Secure the two optical rails on the optical table using four 1/4-20 x 5/16 cap screws and the 3/16 hex balldriver.
|

|
* Prepare four sliding posts, each by attaching one RC1 rail carrier to one PH2-ST post holder with one 1/4-20 x 5/16 cap screws.
|

|

|
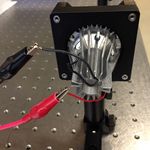
Mount the LED light source:
- In the LCP01 cage plate, the LED will get sandwiched in-between two SM2RR retaining rings. First screw in one SM2RR only 1 mm deep.
- Next place the LED above it.
- Finally tighten down the second SM2RR using the SPW801 adjustable spanner wrench. The SPW801 can be opened until its width matches the SM2RR diameter, the separation between the ring's notches.
- In the LCP02 cage plate adapter, screw in on SM1RR 3 mm deep.
- Carefully (use lens paper unsparingly to protect the lens surface) place the 25 mm plano-convex lens above it, with the hemisphere facing down yet not touching any potentially damaging surface.
- Tighten down a second SM1RR using the SPW602 spanner wrench, whose guide flanges sit in the ring's notches to prevent any scratching of the lens's optical surface.
- Attach the LCP01 cage plate (holding the LED) to the LCP02 adapter (holding the 25 mm condenser lens), using four ER1 rods secured by eight 8-32 set screws.
- Affix a TR2 optical post to the LCP01 cage plate (holding the LED).
- Slide in the LED assembly along the optical rail.
Power the LED light source:
- The red LED will be connected to a DC power supply. Ensure that the current limit on the power supply (CH1) is set to a value below 0.5 A.
- Connect channel CH1 to the red and black threads of the LED, using alligator clip cables.
- Turn on the power supply, and press its Output button to light the LED.
- Adjust the LED brightness using the power supply's Voltage knob.
|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
|

|
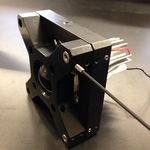
Mount the object (US Air Force target 1951):
- Tighten the R1DS1N 1951 USAF test target in-between two SM1RR retaining rings inside the SM1L10 lens tube, using the SPW602 spanner wrench. (This procedure should be reminiscent of the insertion of the 25 mm hemispherical lens in the cage plate adapter.)
- Slide in the lens tube through the SM1RC slip ring. By rotating the lens tube, you will be able to modify orientation of the object.
- Affix a TR2 optical post to the SM1RC slip ring (holding the USAF target).
- Slide in the object assembly along the optical rail.
|

|
Mount the lens (f = 35 mm):
- Tighten the LB1811 biconvex f = 35 mm lens in-between two SM1RR retaining rings inside the CP02 cage plate.
- Affix a TR2 optical post to the CP02 cage plate (holding the lens).
- Slide in the lens assembly along the optical rail.
|

|

|
Mount the CCD camera:
- Affix a TR2 optical post directly to the CCD camera plate using the 1/4-20 set screw.
- Slide in the camera assembly along the optical rail.
- Connect the CCD to the computer using a red ethernet cable.
- Power up the CCD using the Calrad 45-601 power adapter.
|
| Vertically align the LED, object, lens, and camera assemblies.
|
Capture, save and examine images in Matlab
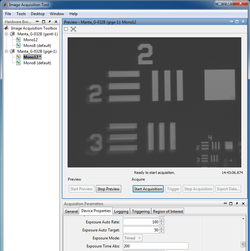
|
- Log on to the computer and run imaqtool in Matlab.
- Select the Manta GigE Mono 12" hardware in the left bar.
- The Start Preview button will bring up a window of the live image from the CCD camera.
- Move the lens and USAF 1951 target object to produce a focused image.
- Measure the distance $ S_o $ from the target object to the lens and the distance $ S_i $ from the lens to the CCD active imaging plane.
|
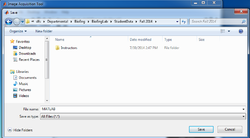
|
- Save images in Matlab:
- Make sure you limit to 1 the number of Frames Per Trigger in the General tab of the Acquisition Parameters;
- Use the Start Acquisition and Export Data buttons;
- Navigate to the Student Data\ Fall 2014\ directory accessible from the computer desktop to be able to access your data remotely, from your home computer for instance.
|
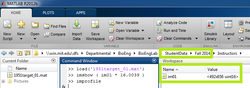
|
align="left"
|
|
align="left"
|
|
align="left"
|
Optical microscopy lab
Code examples and simulations
Background reading
References