Difference between revisions of "Lab Manual: Limits of Detection"
From Course Wiki
Steven Nagle (Talk | contribs) |
Steven Nagle (Talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Category:Lab Manuals]] | [[Category:Lab Manuals]] | ||
[[Category:20.309]] | [[Category:20.309]] | ||
| − | [[Category:Limits of | + | [[Category:Limits of Detection Lab]] |
{{Template:20.309}} | {{Template:20.309}} | ||
Revision as of 18:21, 13 August 2013
Overview
Resolution limit
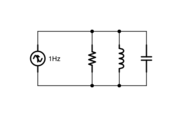
Second order system
- $ \dfrac{1}{Z_{eq}}=\dfrac{1}{Z_R}+\dfrac{1}{Z_L}+\dfrac{1}{Z_C} $
- $ Z_{eq}=\frac{Z_R Z_L Z_C}{Z_R Z_L + Z_R Z_C + Z_L Z_C} $
- $ Z_{eq}=\frac{\hat{V}_o(s)}{\hat{I}_{in}(s)}=\frac{RL/C}{RLs+\dfrac{R}{Cs}+\dfrac{L}{C}}=\frac{Ls}{LCs^2+\dfrac{L}{R}s+1} $
Mechanical circuit analogy
$ \frac{\hat{V}_o(s)}{\hat{F}_{in}(s)}=\frac{\dfrac{1}{m}s}{s^2+ \dfrac{b}{m} s+\dfrac{k}{m} } $