20.109(S21):M1D3
Contents
Introduction:Harvest candidate clones
Protocols:
The yeast that were sorted via FACS in our last lab session were incubated at 30°C for an additional three days so the yeast could recover from the sorting and grow. This additional growth time will give us a sufficient number of cells to harvest plasmid DNA.
Part 1: Harvest plasmid DNA from yeast
To harvest plasmid DNA from yeast we need to do a bit more work to break down the cell wall. Yesterday the 2x107 yeast cells were pelleted and digested with zymolase overnight at 37°C. Zymolase is a mixture of enzymes purified from the bacteria Arthrobacter luteus that degrades the cell wall of yeast and other fungi. The yeast plasmid purification will be carried out using reagents from a commercial kit called Zymoprep MiniPrep II.
- Retrieve your overnight yeast digests from the 37°C incubator.
- Add 200uL of Solution 2 and vortex briefly.
- This is the alkaline buffer.
- Add 400uL of Solution 3, vortex briefly and centrifuge at 14,000g for 10min.
- This is the buffer that neutralizes the pH.
- Transfer the supernatant to a new 1.5 mL tube and centrifuge at 14,000g for an additional 10min.
- Transfer the supernatant to a blue DNA binding, silica column and centrifuge at 10,000g for 30sec. Discard the flow through into a tube labeled 'zymo waste'.
- Add 550uL DNA wash buffer to the column, centrifuge at 10,000g for 2min, and discard the flow through to 'zymo waste'.
- Transfer the column to a new 1.5 mL tube and carefully add 10uL of water to the center of the column to elute the DNA.
- Let the column sit for 2min at room temp.
- Centrifuge at 10,000g for 1min to elute the plasmid DNA from the column and collect the flow-through.
- You will now take your samples to the Nanodrop to measure the DNA's absorbance to quantify the concentration.
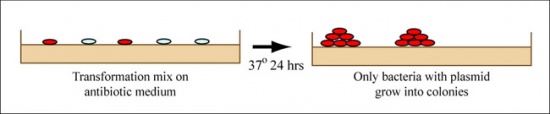
Part 2: Transform plasmid from yeast into E. coli
Competent cells are fragile and should be handled gently, specifically kept cold and not vortexed.
- Label a 1.5 mL tubes with your team information and chill it in your ice bucket.
- Carefully aliquot 25uL of competent NEB 5-alpha E. coli cells from the front laboratory bench in to your cold tube on ice.
- Add 5uL of the yeast plasmid DNA to the competent bacteria.
- Gently tap the tube with your fingertip 5 times to mix.
- Remember: it is important to keep the competent cells cold. Also, avoid over pipetting and vortexing!
- Incubate your transformation mix on ice for 30 min.
- Carry your ice bucket with your transformation to the heat block at the front laboratory bench.
- Be sure you also take your timer.
- Transfer the tube with your transformation to the heat block set to 42 °C and incubate for exactly 30 sec.
- Remove your transformation from the heat block and immediately put them back in the ice bucket, then incubate for 5 min.
- Pipet 500 uL of pre-warmed SOC media into the transformation.
- Move your transformation to the 37 °C incubator and carefully place them on the nutator.
- Incubate transformation for 1 h.
- Retrieve your transformation from the incubator and alert the teaching faculty that you are ready to plate your samples.
- Plate 100μL of the transformation onto an appropriately labeled LB+Amp agar plate.
- The teaching faculty will demonstrate how you should spread the transformation onto the LB+Amp agar plate by using an ethanol burner to sterilize a glass cell spreader.
- Move your spread plate to the 37 °C incubator where they will incubate overnight.
Reagents
- Zymoprep Yeast Plasmid Miniprep II (from Zymo Research)
- Zymolyase
- solution 1
- solution 2
- solution 3
- wash buffer
Next day: [[ ]]