Difference between revisions of "20.109(F20):M1D2"
Noreen Lyell (Talk | contribs) (→Part 2: Treat cells for γH2AX assay) |
Noreen Lyell (Talk | contribs) (→Part 2: Treat cells for γH2AX assay) |
||
| Line 44: | Line 44: | ||
'''H<sub>2</sub>O<sub>2</sub> treatment steps''' | '''H<sub>2</sub>O<sub>2</sub> treatment steps''' | ||
| − | Now that you know what conditions will be tested, the first step in the protocol is to treat the MCL-5 with H<sub>2</sub>O<sub>2</sub>. | + | Now that you know what conditions will be tested, the first step in the protocol is to treat the MCL-5 cells with H<sub>2</sub>O<sub>2</sub>. |
#Retrieve the 12-well plate that was seeded with MCL-5 cells from the 37 °C incubator. | #Retrieve the 12-well plate that was seeded with MCL-5 cells from the 37 °C incubator. | ||
| − | + | STEPS FOR ADHERING CELLS | |
#After aspirating off the media in the wells, add 1 mL of fresh media or media + 20 μM H<sub>2</sub>O<sub>2</sub> to the appropriate wells. | #After aspirating off the media in the wells, add 1 mL of fresh media or media + 20 μM H<sub>2</sub>O<sub>2</sub> to the appropriate wells. | ||
Revision as of 15:57, 15 July 2020
Contents
Introduction
INCLUDE BER PATHWAY DESCRIPTION / PROJECT OVERVIEW
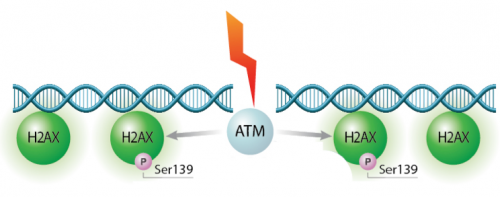
In eukaryotes, including humans, DNA is tightly wound around histone groups. H2AX is a member of the core group of histones that contributes to nucleosome formation and DNA structure. When a DNA double-strand break is introduced into the genome, the H2AX histones near the break are phosphorylated by the ATM kinase at residue Ser-139. Upon phosphorylation H2AX is referred to as gamma-H2AX. Given that only H2AX histones near the site of DNA damage are phosphorylated, γH2AX is a useful target when determining the abundance and location of double-strand breaks.
In your γH2AX assay, you will assess the effects of exposure to H2O2 +/- As.
Protocols
Part 1: Seed cells for γH2AX assay
To ensure the steps required for seeding cells are clear, the Instructor will provide a live demonstration of this process.
In your laboratory notebook, complete the following:
- Provide a written overview / description of the the procedure used to seed cells for the γH2AX assay (from the live demonstration).
- Calculate the volume of cell suspension added to each well for the γH2AX assay.
- The cell suspension is 1 M cells / mL and 25,000 cells were added into each well.
- For how long will the seeded cells incubate prior to treatment with H2O2 +/- As?
Part 2: Treat cells for γH2AX assay
A plate seeded according to the procedure demonstrated in Part 1 was used to treat cells using the H2O2 +/- As conditions detailed below.
Before you read through the protocols for the H2O2 +/- As treatments, it is important to consider what conditions will be assessed in this experiment.
With your laboratory partner, make a list of all of the conditions that will be tested. Use the following descriptions of the variables that are included in this experiment to assist you.
- Two concentrations of H2O2 will be tested: 0 μM and 20 μM
- Three concentrations of As will be tested: 0 μM, 1 μM, and 10 μM
- Each concentration of H2O2 will be tested with each concentration of As.
- Four timepoints will be used for each condition tested: 0 min, 15 min, 30 min, and 60 min.
In your laboratory notebook, complete the following:
- Prepare a list or table of the conditions that will be used for the γH2AX assay.
- What conditions from your list or table are controls? For what does each condition control?
H2O2 treatment steps
Now that you know what conditions will be tested, the first step in the protocol is to treat the MCL-5 cells with H2O2.
- Retrieve the 12-well plate that was seeded with MCL-5 cells from the 37 °C incubator.
STEPS FOR ADHERING CELLS
- After aspirating off the media in the wells, add 1 mL of fresh media or media + 20 μM H2O2 to the appropriate wells.
- Incubate at 37 °C for 1 hour.
In your laboratory notebook, complete the following calculation:
- Calculate the dilution of H2O2 needed to have a final concentration of 20 μM.
- Stock concentration of H2O2 is 10 M.
- Volume of 20 μM H2O2 added to each well is 1 mL.
As treatment steps
- Retrieve the 12-well plate with the H2O2-treated MCL-5 cells from the incubator and use a pipette to remove the media from the wells.
- Add 1 mL of fresh media or media + As to the appropriate wells and incubate at 37 °C for the designated amount of time.
- Following treatment, transfer media to the As waste container and immediately add 400 μL of 4% paraformaldehyde to fix the cells.
- Incubate at room temperature for 10 min.
- Collect the 4% paraformaldehyde in the correct waste stream using a P1000 pipet.
- Wash with 500 μL of 1X PBS.
- Add 1X PBS then remove using a P1000 pipet. Collect the PBS in the correct waste stream.
- Complete a total of 2 times. Leaving 1 mL of 1X PBS on the cells in the final wash.
- Leave all wells with 1 mL PBS, parafilm the sides and move the fixed plates into the 4 °C cooler.
In your laboratory notebook, complete the following calculations:
- Calculate the dilutions of As needed to have final concentrations of 1 μM and 10 μM.
- Stock concentration of As is 100 mM.
- Volume of As solutions added to each well is 1 mL.
Reagents list
- 4% paraformaldehyde (from VWR)
- hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) (from Sigma)
- arsenite (As) (from Sigma)
- phosphate saline buffer (PBS) (from VWR)
Next day: Use immunoflourescence staining to assess repair foci experiment