Difference between revisions of "Flat-field correction"
(Created page with "Category:20.309 Category:Optical Microscopy Lab {{Template:20.309}} ==Overview== Before you record any images from the camera, it is a very good idea to adjust your m...") |
|||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
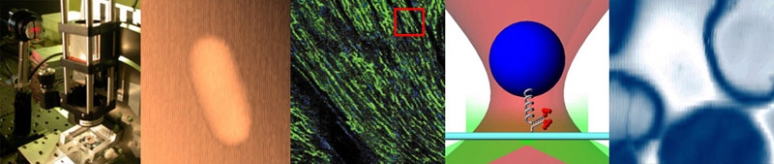
| − | Before you record any images | + | [[File:Nonuniform Illumination.png|thumb|right]] |
| + | Before you record any images, it is a very good idea to adjust your microscope optics to make the illumination is as good as possible. Even if you adjust the illuminator perfectly, the light intensity won't be exactly the same everywhere in the field of view. In most cases, the illumination is brightest in the middle of the image, with a steady decrease in intensity as you approach the edges of the field of view. Dirt or other flaws in the illumination system can also cause variation in the illumination. Another source of non-uniformity is pixel-to-pixel variation in the ''dark level'' and ''responsivity'' of the camera. Because of this, even in complete darkness, all of the pixels on the detector will not necessarily report the same value. Identical light intensities may produce different outputs depending on which pixel on the detector records the signal. These problems can be largely eliminated through a technique called flat-field correction or shading correction. | ||
==Correcting an image== | ==Correcting an image== | ||
Revision as of 02:08, 8 September 2015
Overview
Before you record any images, it is a very good idea to adjust your microscope optics to make the illumination is as good as possible. Even if you adjust the illuminator perfectly, the light intensity won't be exactly the same everywhere in the field of view. In most cases, the illumination is brightest in the middle of the image, with a steady decrease in intensity as you approach the edges of the field of view. Dirt or other flaws in the illumination system can also cause variation in the illumination. Another source of non-uniformity is pixel-to-pixel variation in the dark level and responsivity of the camera. Because of this, even in complete darkness, all of the pixels on the detector will not necessarily report the same value. Identical light intensities may produce different outputs depending on which pixel on the detector records the signal. These problems can be largely eliminated through a technique called flat-field correction or shading correction.