Difference between revisions of "Assignment 8, Part 0: convolution practice"
From Course Wiki
Juliesutton (Talk | contribs) |
Juliesutton (Talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
\end{cases} | \end{cases} | ||
</math> | </math> | ||
| − | * sinc(ax)'' is defined as: <math> \text{sinc}(ax) = \frac{\sin(ax)}{ax}</math> | + | * sinc''(ax)'' is defined as: <math> \text{sinc}(ax) = \frac{\sin(ax)}{ax}</math> |
* rect''(ax)'' is the box function: <math> \text{rect}(ax) = | * rect''(ax)'' is the box function: <math> \text{rect}(ax) = | ||
\begin{cases} | \begin{cases} | ||
| − | 0, & \text{if } | + | 0, & \text{if } |ax|> 1/2 \\ |
| − | 1, & \text{if } | + | 1, & \text{if } |ax| \leq 1/2 |
\end{cases} | \end{cases} | ||
</math> | </math> | ||
Revision as of 17:52, 16 April 2019
| |
Turn in your answers to the following questions |
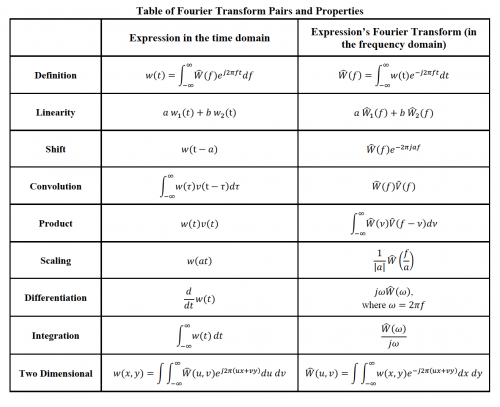
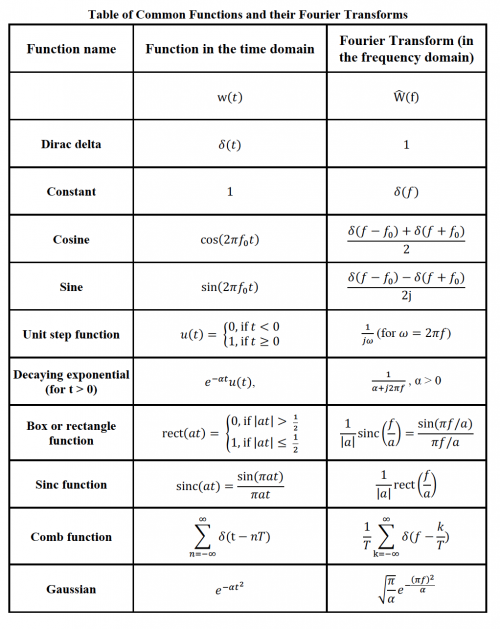
You may find the Fourier transform Tables 8.0.1 and 8.0.2 useful. Note that there are a few functions that you may not have seen before including:
- u(t) is the unit step function $ u(t) = \begin{cases} 0, & \text{if }t<0 \\ 1, & \text{if }t\geq0 \end{cases} $
- sinc(ax) is defined as: $ \text{sinc}(ax) = \frac{\sin(ax)}{ax} $
- rect(ax) is the box function: $ \text{rect}(ax) = \begin{cases} 0, & \text{if } |ax|> 1/2 \\ 1, & \text{if } |ax| \leq 1/2 \end{cases} $
- In class we found the Fourier transform of $ \cos^2(\omega_0 t) $. Use graphical convolution to determine the transform of $ \cos^4(\omega_0 t) $
- Using the transform pairs in table 8.0.2, sketch the fourier transform of $ e^{-\alpha t} u(t) \times \cos(\omega_0 t) $. Assume that $ \alpha\ll\omega_0 $.
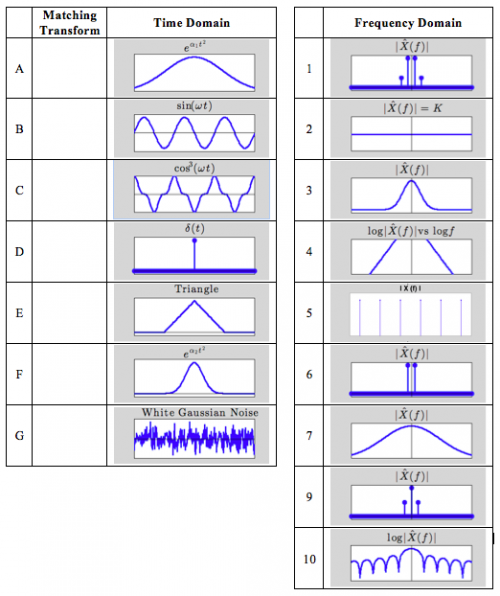
- Table 8.0.3 shows plots of eight time-domain signals A-H. The table on the right includes magnitude plots of the Fourier transform of ten signals numbered 1-10. For each time domain signal A-H, write the number 1-10 in the empty column of the matching frequency-domain signal. You may use a numbered plot more than once.
Some of the frequency plots are shown on log-log axes and some are linear, as indicated by the plot title.
- Overview
- Part 1: feedback systems
- Part 2: fabricate a microfluidic device
- Part 3: add flow control and test your device
Back to 20.309 Main Page