Difference between revisions of "20.109(F19):Treat cells for gamma-H2AX (Day2)"
From Course Wiki
Noreen Lyell (Talk | contribs) (→Navigation links) |
Noreen Lyell (Talk | contribs) (→Protocols) |
||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
==Protocols== | ==Protocols== | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Part 1: Treat cells for γH2AX assay=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Part 2: Prepare CometChip=== | ||
==Reagents list== | ==Reagents list== | ||
Revision as of 16:00, 21 August 2019
Contents
Introduction
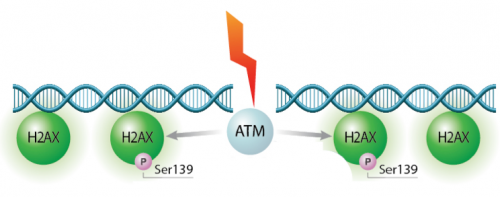
In eukaryotes, including humans, DNA is tightly wound around histone groups. H2AX is a member of the core group of histones that contributes to nucleosome formation and DNA structure. When a DNA double-strand break is introduced into the genome, the H2AX histones near the break are phosphorylated by the ATM kinase at residue Ser-139. Upon phosphorylation H2AX is referred to as gamma-H2AX. Given that only H2AX histones near the site of DNA damage are phosphorylated, γH2AX is a useful target when determining the abundance and location of double-strand breaks.
In your γH2AX assay experiment, you will assess the effects of ...
Protocols
Part 1: Treat cells for γH2AX assay
Part 2: Prepare CometChip
Reagents list
Next day: Complete gamma-H2AX assay and perform loading experiment