Difference between revisions of "Assignment 7, Part 1: op amp golden rules questions"
Juliesutton (Talk | contribs) |
Juliesutton (Talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 37: | Line 37: | ||
<li> | <li> | ||
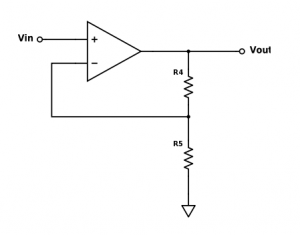
[[Image: VoltageAmp.png|thumb|right|300 px|<caption>(d) Voltage amplifier op amp circuit</caption>]] | [[Image: VoltageAmp.png|thumb|right|300 px|<caption>(d) Voltage amplifier op amp circuit</caption>]] | ||
| − | Even in this new configuration, it will be difficult to obtain an overall gain of 10<sup>8</sup> V/A. The reason is that non-idealities of our op amps will start to creep up at gains much larger than 10<sup>6</sup>. To make up for this, we can amplify the voltage output of the transimpedance amplifier with another op amp circuit (d). Solve for the gain of this circuit, ''V<sub> | + | Even in this new configuration, it will be difficult to obtain an overall gain of 10<sup>8</sup> V/A. The reason is that non-idealities of our op amps will start to creep up at gains much larger than 10<sup>6</sup>. To make up for this, we can amplify the voltage output of the transimpedance amplifier with another op amp circuit (d). Solve for the gain of this circuit, ''V<sub>out</sub> / V<sub>in</sub>'', in terms of the input voltage and the two resistor values. |
</li> | </li> | ||
</ol> | </ol> | ||
Revision as of 18:20, 30 August 2017
This is Part 1 of Assignment 7.
| |
your answers to the following questions |
- Op amp circuits:
-
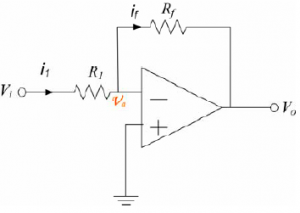
Calculate the gain of circuit (a), Vo / Vi, in terms of the input voltage and the two resistor values.
-
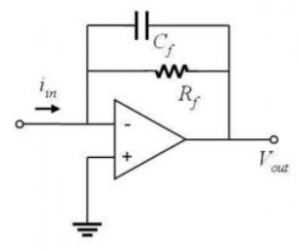
In the DNA melting lab, fluorescence intensity will be determined by measuring the output current of a photodiode. Schematic (b) shows a circuit called a transimpedance amplifier that converts a current to a voltage.
Derive an expression for the output voltage of the circuit produced by a DC current input at iin (b). (At DC, you can ignore the effect of the capacitor.) Express your answer in the form of a transfer function, Vout / iin. - What is the high frequency gain of the transimpedance amplifier shown in Schematic (b)? Remember that a capacitor acts like an open circuit at low frequencies and a short circuit at high frequencies.
- A transimpedance amplifier with a gain of approximately 108 V/A will be required for the DNA melting lab. What value of resistor in the above circuit would achieve this gain?
-
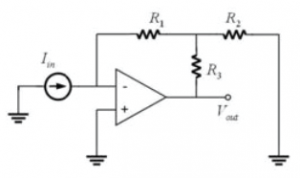
It is undesirable to use the large value of resistor you computed in part A.4. Shown in (c) is another possible implementation of the transimpedance amplifier. Derive an expression for the output voltage of this circuit in terms of the input current and the three resistor values.
- In part A.3., you determined the effect of putting a capacitor across the feedback resistor in a transimpedance amplifier. High gain amplifiers are susceptible to noise coupling from a variety of sources. Since high frequencies are not of interest in the DNA melting lab, it is beneficial to insert a capacitor to reduce the noise. In the above circuit, where would you connect the capacitor and how would you choose its size?
- Now work out the expression for this new circuit's output with respect to the current input for AC signals.
-
Even in this new configuration, it will be difficult to obtain an overall gain of 108 V/A. The reason is that non-idealities of our op amps will start to creep up at gains much larger than 106. To make up for this, we can amplify the voltage output of the transimpedance amplifier with another op amp circuit (d). Solve for the gain of this circuit, Vout / Vin, in terms of the input voltage and the two resistor values.
-
- Simulating DNA melting lab:
- Using DINAmelt or OligoCalc, find an estimate for ΔH0 and ΔS0 for the following oligonucleotide sequence: ATC AAG CAG CCA TCG AAA AAA CT. Assume the complementary strand has no mismatches, the sodium concentration is 100 mM, and the total concentration of oligonucleotide strands is 30 μM.
-
In class, we derived an equation to describe the fraction (f) of double-stranded DNA in solution as a function of temperature (T) in Kelvin as shown below:
$ f = {1 + C_T K_{eq} - \sqrt{1 + 2C_T K_{eq})} \over C_T K_{eq}} $
CT is the total concentration of oligonucleotide strands (30 μM), and Keq is the equilibrium constant as described by the following equation:
$ K_{eq} = e^{ [{\Delta S^0 \over R} - { \Delta H^0 \over RT }]} $
Using these equations and the values you found in part 1, simulate a DNA melting curve, plotting f vs. T. Feel free to use the MATLAB functions given on the wiki page:
http://measurebiology.org/wiki/DNA_Melting:_Simulating_DNA_Melting_-_Basics
</div>
Back to Assignment 7.