Difference between revisions of "20.109(S18):Test protein activity using peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase assay (Day5)"
Noreen Lyell (Talk | contribs) (→Part 1: Prepare samples for PPIase assay) |
Noreen Lyell (Talk | contribs) (→Part 1: Prepare samples for PPIase assay) |
||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
===Part 1: Prepare samples for PPIase assay=== | ===Part 1: Prepare samples for PPIase assay=== | ||
#Calculate dilutions for assay buffer preparation. | #Calculate dilutions for assay buffer preparation. | ||
| − | #* | + | #*You will prepare 6 mL of assay buffer by diluting Tris HCl, pH = 8 and chymotrypsin in H<sub>2</sub>O. |
| − | + | #*Calculate the volume of 1 M Tris HCl, pH = 8 needed for a final concentration of 200 mM. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | #*Calculate the volume of 1 M HCl, pH = 8 needed for a final concentration of 200 mM. | + | |
#*Calculate the volume of 2 μM chymotrypsin needed for a final concentration of 20 nM. | #*Calculate the volume of 2 μM chymotrypsin needed for a final concentration of 20 nM. | ||
| + | #*Calculate the volume of water required to bring the final volume up to 6 mL. | ||
#*Confirm your math with the teaching faculty before proceeding. | #*Confirm your math with the teaching faculty before proceeding. | ||
| − | #Obtain aliquots of 1 M HCl, pH = 8, 2 μM | + | #Obtain aliquots of 1 M Tris HCl, pH = 8, 2 μM chymoptrypsin, and sterile water from the front laboratory bench. |
#Prepare your assay buffer using the calculations completed in Step #1, then chill on ice. | #Prepare your assay buffer using the calculations completed in Step #1, then chill on ice. | ||
| − | #Each team will setup triplicate reactions for | + | #*It is important to keep all of your tubes on ice while your prepare your master mixes. |
| + | #Each team will setup triplicate reactions for '''10''' different conditions: | ||
#*Condition 1: assay buffer with suc-AAFP-pNA substrate | #*Condition 1: assay buffer with suc-AAFP-pNA substrate | ||
| − | #*Condition 2: assay buffer with suc-AAFP-pNA substrate AND FKBP12 protein | + | #*Condition 2: assay buffer with suc-AAFP-pNA substrate AND '''your''' FKBP12 protein |
| − | #*Condition 3: assay buffer with suc-AAFP-pNA substrate AND FKBP12 protein AND rapamycin | + | #*Condition 3: assay buffer with suc-AAFP-pNA substrate AND '''your''' FKBP12 protein AND rapamycin |
| − | #*Condition 4: assay buffer with suc-AAFP-pNA substrate AND FKBP12 protein AND ligand #1 | + | #*Condition 4: assay buffer with suc-AAFP-pNA substrate AND '''your''' FKBP12 protein AND ligand #1 |
| − | #*Condition 5: assay buffer with suc-AAFP-pNA substrate AND FKBP12 protein AND ligand #2 | + | #*Condition 5: assay buffer with suc-AAFP-pNA substrate AND '''your''' FKBP12 protein AND ligand #2 |
| − | # | + | #*Condition 6: assay buffer with suc-AAFP-pNA substrate AND '''Abcam''' FKBP12 protein |
| − | #Next, | + | #*Condition 7: assay buffer with suc-AAFP-pNA substrate AND '''Abcam''' FKBP12 protein AND rapamycin |
| − | + | #*Condition 8: assay buffer with suc-AAFP-pNA substrate AND '''Abcam''' FKBP12 protein AND ligand #1 | |
| − | #Calculate the volume of 40% DMSO needed for a final concentration of 0.2% (volume:volume) using the final reaction volume of 200 μL. | + | #*Condition 9: assay buffer with suc-AAFP-pNA substrate AND '''Abcam''' FKBP12 protein AND ligand #2 |
| − | + | #Clearly label 9 1.5 mL centrifuge tubes, one for each condition. | |
| − | #* | + | #Next, calculate the volumes of each reagent needed for each condition. |
| − | + | #*Calculate the volume of 40% DMSO needed for a final concentration of 0.2% (volume:volume) using the final reaction volume of 200 μL. Because DMSO is used to dissolve rapamycin and the ligands, it must be included to reduce unintended variables into the experiment. | |
| − | #* | + | #*Calculate the volume of 20 μM rapamycin needed for a final concentration of 0.1 μM using the final reaction volume of 200 μL. |
| − | + | #*Calculate the volume of each 8 mM ligand needed for a final concentration of 40 μM using the final reaction volume of 200 μL. | |
| − | # | + | #In your notebook, make a chart / list indicating which reagents will be added to make the master mixes for the conditions and include the volume of each. |
| − | # | + | #*Prepare enough master mix for 3.25 reactions (you will test each condition in triplicate, but should prepare excess master mix to account for pipetting errors). |
| − | #*When told to do so, | + | #*For '''your''' protein (Conditions #2 - #5), add 10 μL of '''your''' FKBP12 and 169 μL of assay buffer per reaction. |
| + | #*For '''Abcam''' protein (Conditions #6 - #9), add 1 μL of '''Abcam''' FKBP12 and 178 μL of assay buffer per reaction. | ||
| + | #*For all other reagents (DMSO, rapamycin, and ligands), use the volumes you calculated in Step #5. | ||
| + | #Confirm your calculations with the teaching faculty before you proceed! | ||
| + | #Prepare your master mix for each Condition by adding all appropriate reagents, '''except''' protein. | ||
| + | #*Alert the teaching faculty when this step is completed. | ||
| + | #When told to do so, add the appropriate protein to the master mix for each Condition. | ||
| + | #You will transfer your master mixes into a 96-well plate on the front laboratory bench. | ||
| + | #The teaching faculty will tell you which wells to use as three teams will add their samples in the same plate. | ||
| + | #*Transfer 180 μL of each master mix into 3 wells according to the plate map. | ||
| + | #*'''Be mindful that you are adding your samples to the correct wells!''' | ||
After all teams have loaded their samples, the teaching faculty will add 20 μL of the suc-AAFP-pNA substrate (5 mM in TFE containing 460 mM LiCl) to the samples and immediately load the plate onto the plate reader. The plate reader will record the 405 nm values at 25 °C for each sample every minute for 30 minutes (a total of 31 readings including t = 0). | After all teams have loaded their samples, the teaching faculty will add 20 μL of the suc-AAFP-pNA substrate (5 mM in TFE containing 460 mM LiCl) to the samples and immediately load the plate onto the plate reader. The plate reader will record the 405 nm values at 25 °C for each sample every minute for 30 minutes (a total of 31 readings including t = 0). | ||
Revision as of 21:00, 16 February 2018
Contents
Introduction
Today you will test the activity of FKBP12 using a peptidyl-prolyl isomerase (PPIase) assay. PPIases catalyze cis-trans isomerization reactions that are essential to efficient protein folding in vivo. Specifically, these enzymes isomerize peptide bonds that are N-terminal to proline residues in polypeptide chains. Without PPIases, isomerization would be the rate-limiting step in protein folding.
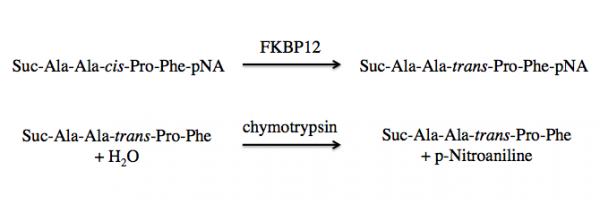
FKBP12 is a class of PPIases and the activity can be measured by quantifying the isomerization and subsequent cleavage of a substrate, suc-AAFP-pNA (also written as Suc-Ala-Ala-Pro-Phe-NA). In this method, FKBP12 catalyzes the isomeration of the cis-Ala-Pro bond to a trans-Ala-Pro bond. Then a second enzyme, chymytrypsin, cleaves the trans form of the peptide. See the reaction schematic below.
When at equilibrium in solution, approximately 88% of the commercially available suc-AAFP-pNA substrate is in the trans from, leaving only a small amount of the peptide for isomerization. Because of this, the suc-AAFP-pNA substrate is prepared in trifluoroethanol (TFE) containing lithium chloride, LiCl. The Li+ ions maintain the substrate in 60% cis form.
Upon cleavage by chymotrypsin, the release of p-nitroaniline results in a yellow color in alkaline conditions that can be measured at 405 nm. The rate of Δ405 nm in the presence versus absence of FKBP12 is used to calculate the activity.
Protocols
Part 1: Prepare samples for PPIase assay
- Calculate dilutions for assay buffer preparation.
- You will prepare 6 mL of assay buffer by diluting Tris HCl, pH = 8 and chymotrypsin in H2O.
- Calculate the volume of 1 M Tris HCl, pH = 8 needed for a final concentration of 200 mM.
- Calculate the volume of 2 μM chymotrypsin needed for a final concentration of 20 nM.
- Calculate the volume of water required to bring the final volume up to 6 mL.
- Confirm your math with the teaching faculty before proceeding.
- Obtain aliquots of 1 M Tris HCl, pH = 8, 2 μM chymoptrypsin, and sterile water from the front laboratory bench.
- Prepare your assay buffer using the calculations completed in Step #1, then chill on ice.
- It is important to keep all of your tubes on ice while your prepare your master mixes.
- Each team will setup triplicate reactions for 10 different conditions:
- Condition 1: assay buffer with suc-AAFP-pNA substrate
- Condition 2: assay buffer with suc-AAFP-pNA substrate AND your FKBP12 protein
- Condition 3: assay buffer with suc-AAFP-pNA substrate AND your FKBP12 protein AND rapamycin
- Condition 4: assay buffer with suc-AAFP-pNA substrate AND your FKBP12 protein AND ligand #1
- Condition 5: assay buffer with suc-AAFP-pNA substrate AND your FKBP12 protein AND ligand #2
- Condition 6: assay buffer with suc-AAFP-pNA substrate AND Abcam FKBP12 protein
- Condition 7: assay buffer with suc-AAFP-pNA substrate AND Abcam FKBP12 protein AND rapamycin
- Condition 8: assay buffer with suc-AAFP-pNA substrate AND Abcam FKBP12 protein AND ligand #1
- Condition 9: assay buffer with suc-AAFP-pNA substrate AND Abcam FKBP12 protein AND ligand #2
- Clearly label 9 1.5 mL centrifuge tubes, one for each condition.
- Next, calculate the volumes of each reagent needed for each condition.
- Calculate the volume of 40% DMSO needed for a final concentration of 0.2% (volume:volume) using the final reaction volume of 200 μL. Because DMSO is used to dissolve rapamycin and the ligands, it must be included to reduce unintended variables into the experiment.
- Calculate the volume of 20 μM rapamycin needed for a final concentration of 0.1 μM using the final reaction volume of 200 μL.
- Calculate the volume of each 8 mM ligand needed for a final concentration of 40 μM using the final reaction volume of 200 μL.
- In your notebook, make a chart / list indicating which reagents will be added to make the master mixes for the conditions and include the volume of each.
- Prepare enough master mix for 3.25 reactions (you will test each condition in triplicate, but should prepare excess master mix to account for pipetting errors).
- For your protein (Conditions #2 - #5), add 10 μL of your FKBP12 and 169 μL of assay buffer per reaction.
- For Abcam protein (Conditions #6 - #9), add 1 μL of Abcam FKBP12 and 178 μL of assay buffer per reaction.
- For all other reagents (DMSO, rapamycin, and ligands), use the volumes you calculated in Step #5.
- Confirm your calculations with the teaching faculty before you proceed!
- Prepare your master mix for each Condition by adding all appropriate reagents, except protein.
- Alert the teaching faculty when this step is completed.
- When told to do so, add the appropriate protein to the master mix for each Condition.
- You will transfer your master mixes into a 96-well plate on the front laboratory bench.
- The teaching faculty will tell you which wells to use as three teams will add their samples in the same plate.
- Transfer 180 μL of each master mix into 3 wells according to the plate map.
- Be mindful that you are adding your samples to the correct wells!
After all teams have loaded their samples, the teaching faculty will add 20 μL of the suc-AAFP-pNA substrate (5 mM in TFE containing 460 mM LiCl) to the samples and immediately load the plate onto the plate reader. The plate reader will record the 405 nm values at 25 °C for each sample every minute for 30 minutes (a total of 31 readings including t = 0).
Part 2: Calculate activity of FKBP12
The data for your PPIase experiment will be provided as an excel spreadsheet that includes the 405 nm values for each well at every timepoint. You are responsible for the data analysis of only your samples, not for the entire plate.
- Average the triplicate wells for each condition you tested at every timepoint.
- Plot the averaged values (x-axis) over time (y-axis) for each condition.
- Use the t = 0 and t = 30 to calculate the activity of FKBP12 condition tested.
- TEST = Condition 2 - 5, and BLANK = Condition 1.
- Be sure to use the appropriate value for minutes given the t values.
- The calculations are completed for each condition separately.
- Post the units / mg protein value calculated for each condition to Class data page.
- In addition, email your spreadsheet (with the plot and calculations) to the teaching faculty.
Reagents
- FKBP12 (1 mg/mL), Abcam
- chymotrypsin, Sigma
- suc-AAFP-pNA, Sigma
- rapamycin, Sigma
- ligands, Chembridge
Next day: Confirm ligand binding using differential scanning fluorimetry assay